AI in Robotics: A Comprehensive Overview
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing robotics, equipping machines with the ability to perform tasks with unparalleled precision, efficiency, and autonomy. From manufacturing and healthcare to agriculture and logistics, AI-powered robots are reshaping industries and improving our daily lives. This comprehensive overview explores the key components, applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends of AI in robotics.
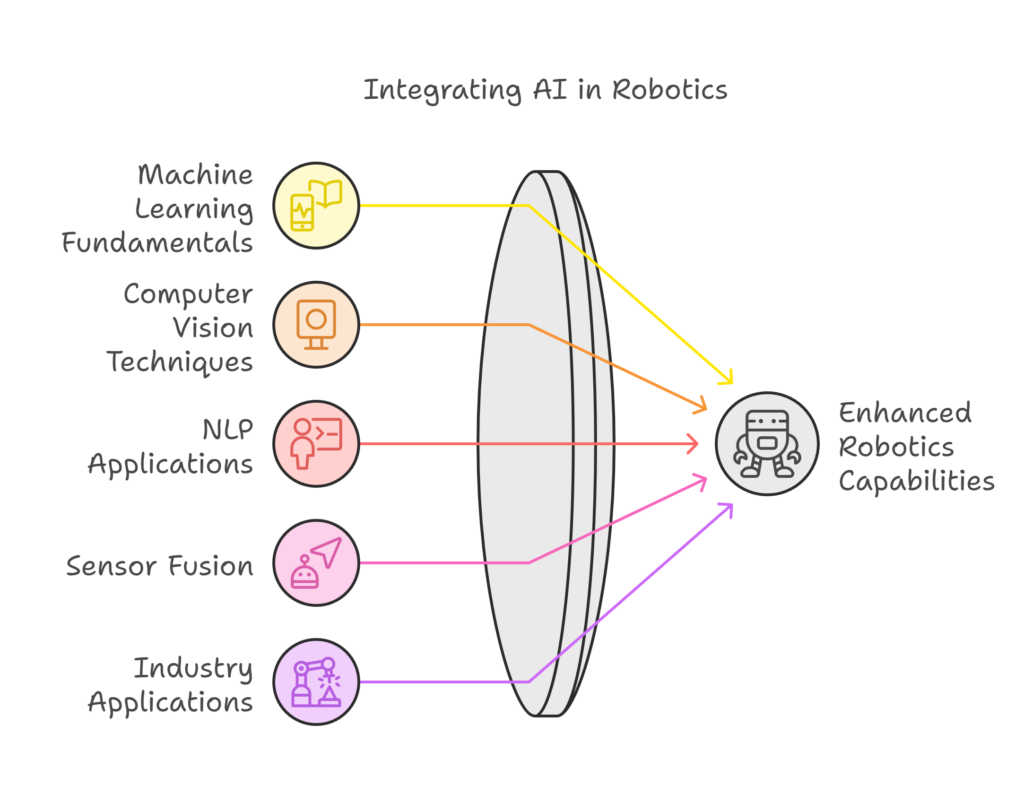
Understanding the Fundamentals of AI in Robotics
AI in robotics relies on several foundational technologies:
1. Machine Learning (ML)
ML enables robots to learn from data and improve performance over time without explicit programming. Common ML techniques in robotics include:
- Supervised Learning: Using labeled datasets to teach robots pattern recognition and predictive tasks.
- Unsupervised Learning: Identifying hidden structures in unlabeled data to understand patterns.
- Reinforcement Learning: Employing trial-and-error methods, where robots optimize actions based on rewards and punishments.
2. Computer Vision
Computer vision equips robots with the ability to “see” and interpret their environment. Using deep learning models like convolutional neural networks (CNNs), robots can identify objects, navigate spaces, and perform precision tasks, such as detecting defects in manufacturing or assisting in complex surgeries.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP allows robots to understand and respond to human language. This capability enhances human-robot interaction by enabling robots to execute voice commands and engage in meaningful conversations.
4. Sensor Fusion
Sensor fusion integrates data from multiple sensors—such as cameras, LiDAR, and ultrasonic sensors—to create a detailed understanding of the environment. This holistic approach allows robots to operate efficiently even in challenging and dynamic settings.
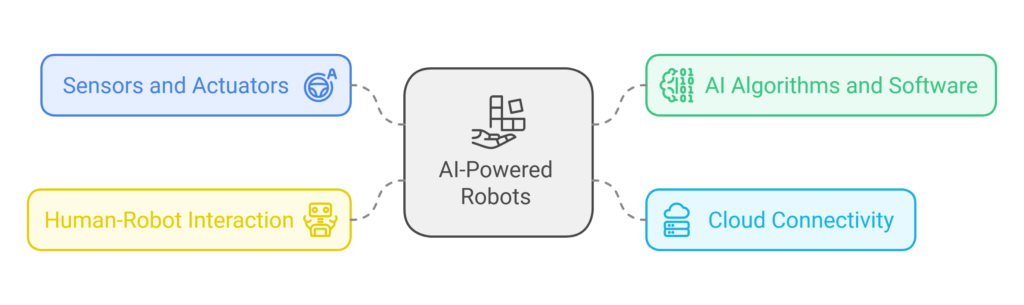
Key Components of AI-Powered Robots
AI-powered robots comprise several critical components:
- Sensors and Actuators: Sensors collect data from the robot’s surroundings, while actuators enable movement and interaction. Examples include cameras, LiDAR for vision, and robotic arms for physical manipulation.
- AI Algorithms and Software: These serve as the robot’s “brain,” processing sensory input, making decisions, and guiding actions. Popular tools include TensorFlow for AI modeling and Robot Operating System (ROS) for robot programming.
- Cloud Connectivity: Cloud platforms provide real-time data processing, updates, and coordination for robot fleets, facilitating advanced learning and scalability.
- Human-Robot Interaction (HRI): User-friendly interfaces ensure seamless collaboration, whether through touchscreens, voice commands, or gesture-based controls.
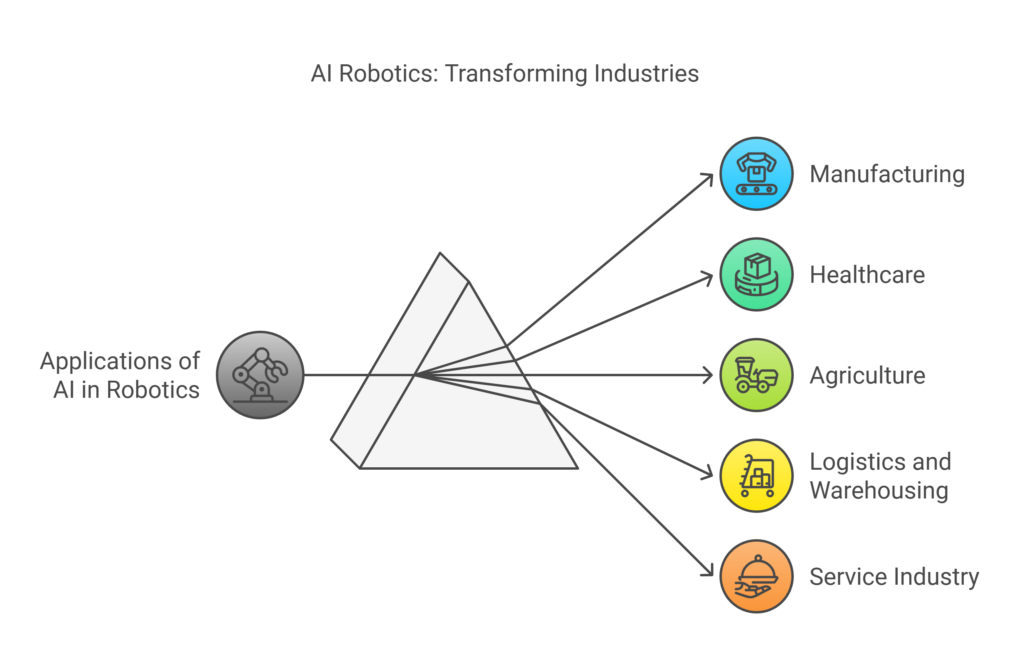
Applications of AI in Robotics Across Industries
1. Manufacturing
AI robots excel in tasks like:
- Automating assembly lines
- Performing quality inspections
- Collaborating with human workers as cobots (collaborative robots)
2. Healthcare
AI-powered robots are enhancing healthcare through:
- Surgical Assistance: Precision-guided robotic surgeries
- Patient Rehabilitation: Recovery aids for mobility and physical therapy
- Elder Care: Monitoring vitals, medication reminders, and companionship
3. Agriculture
AI robotics is driving smart farming:
- Autonomous tractors for planting and harvesting
- Drones for crop health monitoring
- Robots implementing precision farming to reduce waste
4. Logistics and Warehousing
Key innovations include:
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for efficient material movement
- Robots for inventory management and last-mile delivery
5. Service Industry
Robots enhance customer service and operations by:
- Handling cleaning and maintenance
- Assisting customers in retail and hospitality
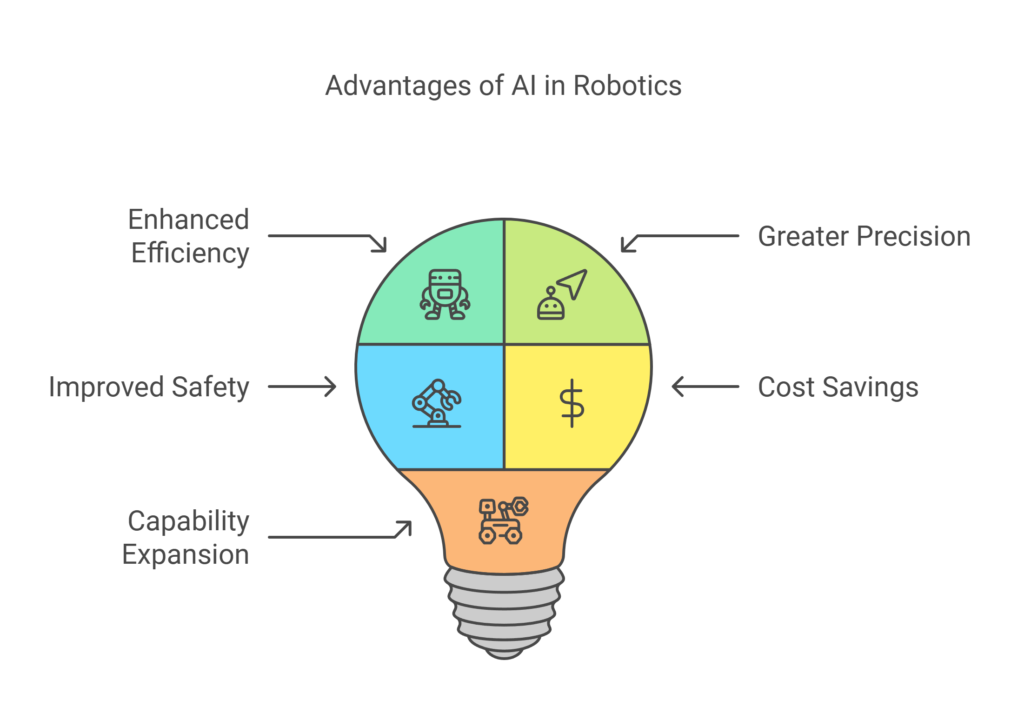
Benefits of AI in Robotics
The integration of AI into robotics offers numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Robots can work 24/7 with consistent output.
- Greater Precision: Tasks are performed with high accuracy, reducing errors.
- Improved Safety: Robots take on hazardous jobs, minimizing risks for humans.
- Cost Savings: Automation reduces labor costs and enhances predictive maintenance.
- Capability Expansion: Robots can tackle complex tasks that were once impossible for machines.
Generative AI for Software Developers Specialization
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, AI in robotics faces challenges:
Technical Challenges
- Developing reliable AI algorithms for unpredictable environments
- Managing the high energy consumption of mobile robots
Ethical and Social Concerns
- Job displacement due to automation
- Privacy risks associated with data collection
- Accountability for autonomous decisions
Implementation Hurdles
- High initial investment costs
- Training personnel to operate and maintain robots
- Integrating robots with existing systems
Future Trends in AI Robotics
The future of AI in robotics is promising:
- Advancements in Deep Learning: Enabling robots to learn more complex behaviors and adapt faster.
- Edge AI: Localized data processing for faster decision-making and reduced reliance on cloud connectivity.
- Human-Robot Collaboration: Robots working alongside humans to complement their abilities rather than replace them.
- Sustainable Robotics: Energy-efficient designs and biodegradable materials for eco-friendly robots.
Conclusion
AI is undeniably transforming robotics, empowering machines with unparalleled capabilities. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements in AI technologies will continue to shape a future where robots play an even greater role in industries and society. Whether improving healthcare outcomes, enhancing productivity, or enabling safer operations, the synergy of AI and robotics holds immense potential for innovation and growth.
Explore our blog series on AI Applications Across Industries to learn more about how this transformative technology is reshaping our world.
Dive deeper into related topics like AI in Manufacturing and The Role of Robotics in Healthcare Innovation to stay ahead of the curve!
Summary of AI in Robotics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing robotics, empowering machines with the ability to learn, adapt, and execute complex tasks. Here’s a structured overview of AI’s transformative impact on robotics, its technologies, applications, and challenges:
1. Key Technologies Driving AI in Robotics
- Machine Learning (ML):
Robots use ML to learn from data and improve over time. Key techniques include:- Supervised Learning: Learning with labeled datasets.
- Unsupervised Learning: Identifying patterns in unlabeled data.
- Reinforcement Learning: Learning by trial and error to maximize rewards.
- Computer Vision:
Powered by deep learning and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), computer vision enables robots to interpret visual data for object recognition, navigation, and task execution. - Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP allows robots to understand and respond to human language, enhancing communication through voice commands or text interfaces. - Sensor Fusion:
Integrating data from multiple sensors (e.g., cameras, LiDAR) provides robots with a comprehensive view of their surroundings for better decision-making.
2. Components of AI-Powered Robots
- Sensors and Actuators: Sensors gather data, while actuators enable robots to interact with their environment.
- AI Algorithms and Software: Frameworks like TensorFlow and ROS serve as the “brain” of the robots, driving intelligent decision-making.
- Cloud Connectivity: Offers access to extensive computational resources and real-time updates.
- Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) Interfaces: Facilitates seamless communication, ranging from control panels to advanced multimodal systems.
3. Applications Across Industries
- Manufacturing:
- Automating assembly lines.
- Enhancing quality control.
- Enabling human-robot collaboration through cobots.
- Healthcare:
- Improving surgical precision.
- Supporting patient rehabilitation.
- Assisting in eldercare.
- Agriculture:
- Smart farming via autonomous tractors.
- Crop monitoring and precision farming techniques.
- Logistics and Warehousing:
- Automating inventory management.
- Optimizing material movement.
- Handling last-mile deliveries.
- Service Industry:
- Performing cleaning and maintenance tasks.
- Enhancing customer service experiences.
4. Benefits of AI in Robotics
- Increased productivity and efficiency.
- Enhanced accuracy in task execution.
- Improved safety, especially in hazardous environments.
- Cost reductions in operations.
- Ability to handle complex decision-making.
5. Challenges and Considerations
- Technical Challenges:
- Robust algorithm development for unpredictable environments.
- Ensuring safety in human-robot interactions.
- Managing power demands of AI systems.
- Ethical Concerns:
- Job displacement.
- Privacy and data security.
- Liability in autonomous decision-making.
- Integration Issues:
- High initial implementation costs.
- Training and maintenance challenges.
- Compatibility with existing systems.
6. Case Study: Kanerika’s AI-powered RPA
Kanerika implemented AI-powered robotic process automation (RPA) for fraud detection in insurance. The system reduced manual work, improved accuracy, and enhanced fraud identification, showcasing the potential of AI in practical applications.
7. FAQs on AI in Robotics
- What is AI in robotics?
AI equips robots with intelligence to perform complex tasks autonomously. - How is AI used in robotics?
Through technologies like ML, computer vision, and NLP, AI enhances robotics across industries. - What are the benefits of AI in robotics?
Improved efficiency, accuracy, safety, and cost-effectiveness. - What are the challenges?
Ethical concerns, technical hurdles, and integration complexities.
Relevant Links for Deep Dives
Learn from experts at Google and get in-demand AI skills you can apply to your work right away with Google AI Essentials, zero experience required.
- Machine Learning and Robotics Fundamentals
- Computer Vision in Robotics
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Sensor Fusion and Navigation
- Applications Across Industries
.








Leave a Reply